In this article you will learn, among other things, why age warts develop, how you can recognize them in good time and what options there are for removing them.
What are Age warts?
The term "senile warts" is misleading, as these are not actually real warts. Genuine warts are caused by viruses, whereas senile warts, also known as basal cell papillomas, develop without viral influence and are therefore not contagious. Age warts, which are medically referred to as seborrhoeic keratoses, are benign tumors on the surface of the skin that are caused by a change in the top layer of the skin (epidermis). These skin changes mainly occur at an advanced age. They are medically harmless, but can be perceived as disturbing due to their appearance.
Why do age-related warts develop?
The exact causes for the development of senile warts are not yet fully understood. However, there are several factors that can promote the development of these skin changes:
Genetic predisposition
Genetic predisposition appears to be an important factor in the development of senile warts. If senile warts run in the family, there is a higher probability that subsequent generations will also be affected. However, this does not mean that senile warts are necessarily inherited, but rather that there is a genetic abnormality.
Age-related changes to the skin
As we age, the skin changes in many ways. Cell division and regeneration of the skin slows down, which can lead to an accumulation of horny cells in the upper layers of the skin. This excessive keratinization (hyperkeratosis) is one of the main causes of age-related warts.
UV radiation
Although age-related warts are not directly caused by sun exposure, long-term UV exposure could promote the development of these skin changes. Scientific studies indicate that skin areas that are frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face or neck, are more likely to develop age-related warts. This underlines the importance of consistent sun protection, especially at an advanced age.
Mechanical irritation
In some cases, age warts can appear in areas that are frequently exposed to mechanical friction, such as under tight clothing or in areas that are regularly subjected to pressure. This friction can stimulate the growth of skin cells and thus promote the formation of age warts.
When and where do senile warts develop?
Age-related warts usually appear from the age of 40 and their frequency increases with age. They can appear on various parts of the body, although some areas are particularly frequently affected:
- Face: Especially in the forehead area, on the cheeks and around the eyes.
- Neck and nape: These areas are vulnerable due to their constant exposure to sunlight.
- Back and chest: Age-related warts often appear on the upper back and under the breasts.
- Arms and legs: Less common, but not uncommon, are age-related warts on the extremities.
In addition, senile warts do not typically appear on the palms of the hands or soles of the feet, which is an important distinguishing feature from other skin changes.
Early appearance of senile warts
In some cases, senile warts can appear as early as the 30s. This is not usually a cause for concern and indicates a genetic predisposition. However, an early appearance could also indicate increased sun exposure or mechanical irritation.
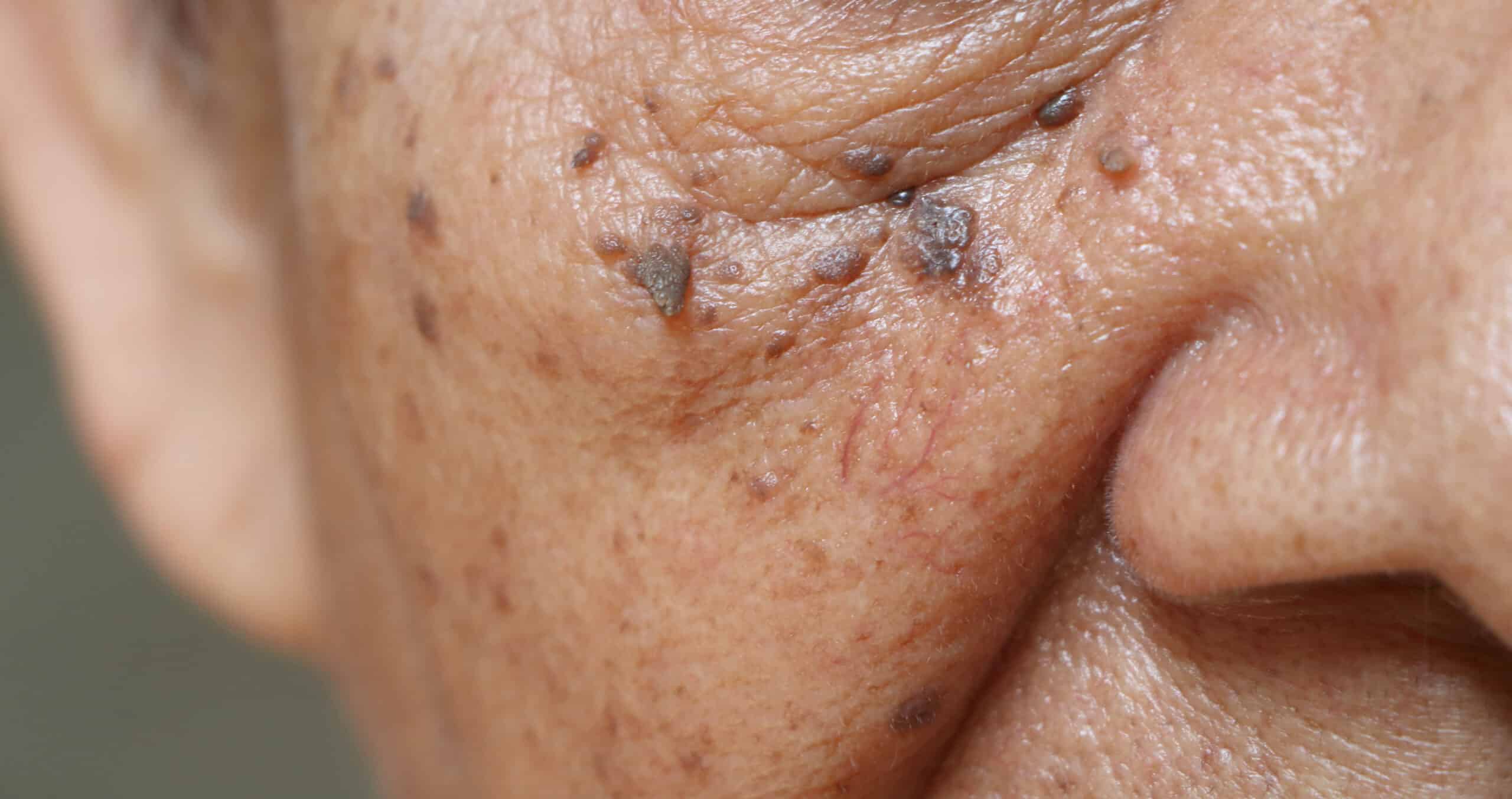
Symptoms: How do age-related warts appear?
Age-related warts are easy to recognize due to their roundish or oval shape and their wart-like, often greasy surface. They usually have a diameter of half a centimeter to one centimeter, but can also be larger or smaller. Age-related warts are sharply demarcated from the surrounding tissue and can have a flat or raised surface. Their color varies from light brown to dark brown to black. Sometimes they can also take on reddish tones.
Variants of senile warts
In addition to the typical age-related warts, there are also some less common variants:
- Stucco keratosis: These age warts are flat, rather light in color and have white scales that can be easily scraped off. They usually occur more frequently on the back of the foot, ankle or lower leg and affect men more often.
- Melanoacanthoma: These age-related warts are particularly dark and heavily pigmented.
- Verruca plana-like keratosis: These flat, dark age warts often appear on the back of the hands and forearms, especially in people whose skin has been damaged by UV radiation.
- Dermatosis papulosa nigra: This form occurs particularly in women and darker skin types and often appears on the face, neck, chest or nape of the neck. It occurs more frequently in families.
- Reader-Trélat syndrome: These age-related warts suddenly appear in large numbers and can be accompanied by itching. Although they are benign, they can occur as a side effect of cancer.
Differential diagnosis
It is important not to confuse age warts with other skin changes that could be potentially dangerous, such as skin cancer. In some cases, age warts can have similar characteristics to malignant tumors, which is why a thorough examination by a dermatologist is necessary. Among other things, a distinction must be made between:
- Dermatofibroma: A hard fibroma that often appears on the arms or legs and can easily be mistaken for a mole.
- Bowen's disease/actinic keratosis: These skin changes are precursors of white skin cancer and often appear in the form of reddish, scaly skin with clear boundaries.
- Spinocellular carcinoma: Also known as prickle cell carcinoma, it is a form of malignant skin cancer characterized by red, crusty patches of skin.
- Basal cell carcinoma: A slow-growing skin cancer that often has the same color as the surrounding skin and grows in depth.
- Black skin cancer (melanoma): This aggressive cancer often appears as a dark or black spot and may be flat or raised.
If there is any doubt about the diagnosis, the doctor can take a tissue sample and have the skin change examined more closely in the laboratory.
What can you do about age-related warts?
Age-related warts are generally harmless and do not necessarily need to be removed. However, many people decide to have them removed, especially if the warts are aesthetically unpleasant or are located in areas that are regularly irritated.
Prevention of senile warts
Although there is no sure way to completely prevent age-related warts, some measures can reduce the risk of them developing:
- Sun protection: Regular use of sunscreen can help to protect the skin from UV radiation and reduce the risk of age-related warts.
- Skin care: A good skin care routine with moisturizing creams and scrubs can help to keep the skin smooth and healthy.
- Avoidance of irritation: Avoid tight clothing that could rub and irritate the skin to minimize the development of new age warts.
Removal of senile warts
There are various methods for removing age warts. The choice of method depends on the size, number and location of the warts as well as the patient's individual preferences.
Laser removal
Laser wart removal is a modern and very effective method that is particularly suitable for visible skin areas such as the face.
Functionality
During laser treatment, a special laser is directed at the wart. The laser beam vaporizes the uppermost layers of skin where the wart is located, removing it precisely and gently. The skin remains as intact as possible, which facilitates healing.
Advantages and disadvantages
- Advantages: Laser removal is minimally invasive and generally leaves no scars. It is particularly suitable for sensitive skin areas such as the face.
- Disadvantages: The costs for laser treatment are higher compared to the alternatives.
Surgical removal
Surgical removal of senile warts is a proven method that is used in particular for large or deep warts.
Functionality
During surgical removal, the wart is removed with a scalpel or curette. This is done under local anesthesia and allows the wart to be removed immediately.
Advantages and disadvantages
- Advantages: This method is very effective and enables a histological examination of the removed tissue to ensure that it is a benign change.
- Disadvantages: There is a small risk of scarring and the healing time may take longer.
Icing (cryotherapy)
Icing is a method in which the senile wart is treated with liquid nitrogen. The extremely low temperatures cause the tissue to die and the wart falls off by itself after a few days.
Advantages and disadvantages
- Advantages: Icing is a simple and quick method that does not require any incisions.
- Disadvantages: Redness and blistering may occur and in some cases re-treatment may be necessary.
Home remedy
Many people try to remove age warts with home remedies, such as apple cider vinegar, tea tree oil or aloe vera. However, these methods are usually ineffective and can irritate the skin. It is therefore advisable to have age warts removed by a dermatologist after the age warts have been diagnosed as such beyond doubt.
If you are interested in more information about age-related warts, it is advisable to seek advice from an experienced dermatologist. At Hautwerk in Zurich, we offer professional consultations and treatments that are individually tailored to your skin needs. Don't hesitate to make an appointment to find the best solution for your skin.